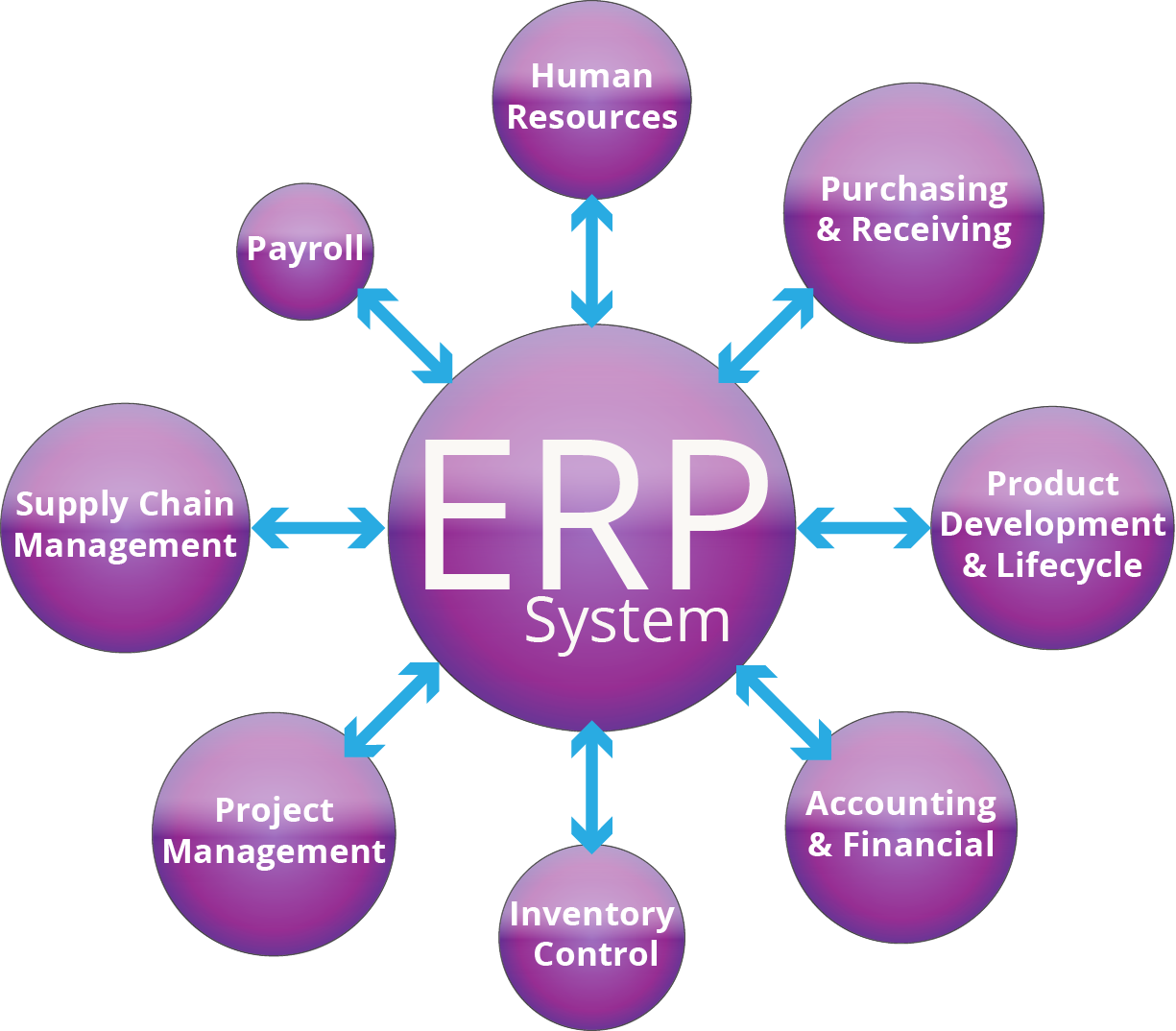
Welcome to our guide on Essential ERP System Requirements Checklist! If you are a business looking to streamline your operations and improve efficiency, implementing an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system can be a game-changer. However, selecting the right ERP system can be a daunting task with so many options available in the market. In this article, we will break down the key requirements you need to consider before choosing an ERP system for your business.
Functional requirements for ERP systems
When it comes to selecting an ERP system for your business, it is crucial to consider the functional requirements that will meet your organization’s needs. These requirements are the specific tasks and processes that the ERP system must be able to handle in order to improve efficiency, accuracy, and overall operations. Let’s delve into some of the key functional requirements that you should keep in mind:
1. Financial Management: One of the most important functional requirements for an ERP system is its ability to manage financial processes effectively. This includes features such as general ledger management, accounts payable and receivable, budgeting, and financial reporting. The system should be able to streamline financial transactions, ensure compliance with regulations, and provide real-time visibility into the financial health of the organization. It should also support multiple currencies and languages, especially if your business operates internationally.
Furthermore, the ERP system should offer robust financial analysis tools that can help identify trends, forecast future performance, and make informed strategic decisions. It should integrate seamlessly with other modules such as inventory management, sales, and procurement to provide a complete picture of the financial impact of various business activities. Make sure to assess the scalability of the financial management function to ensure that it can handle the growth of your business.
In addition, the ERP system should have features for managing fixed assets, handling tax calculations, and generating financial statements in accordance with accounting standards. Security controls should be in place to protect sensitive financial data and prevent unauthorized access. The system should also allow for customization and configuration to adapt to the unique financial requirements of your business.
In summary, a comprehensive financial management module is essential for an ERP system to effectively support the financial operations of your business. It should provide a centralized platform for managing all financial processes, ensuring accuracy, compliance, and visibility into the financial health of the organization.
Technical requirements for ERP systems
When considering the technical requirements for ERP systems, there are several key factors to take into account. One important aspect to consider is the hardware requirements. This includes the server infrastructure needed to support the ERP system, as well as the network requirements for connectivity. The hardware should be scalable to accommodate growth in the number of users and the volume of data processed by the system. It should also be reliable and secure to ensure the integrity of the data stored within the ERP system.
In addition to hardware requirements, it is also essential to consider the software requirements for an ERP system. This includes the compatibility of the ERP software with the operating system and database management system being used by the organization. The ERP software should also be able to integrate seamlessly with other systems and applications used within the organization, such as accounting software, CRM systems, and e-commerce platforms.
Another important technical requirement for ERP systems is data migration and integration capabilities. The ERP system should be able to efficiently import and export data from external sources, such as legacy systems or third-party applications. It should also have robust data integration tools to ensure that data is accurately synchronized across different modules within the ERP system.
Scalability is another key technical requirement for ERP systems. As the organization grows and evolves, the ERP system should be able to scale to accommodate the changing needs of the business. This includes the ability to add new users, modules, and functionality to the system without causing any disruptions to the existing processes.
Security is also a critical technical requirement for ERP systems. The ERP system should have built-in security features to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. This includes user authentication, role-based access control, data encryption, and audit trails to track any changes made to the system.
Lastly, it is important to consider the technical support and maintenance requirements for an ERP system. The organization should have access to a reliable support team that can provide assistance with troubleshooting issues, implementing updates, and optimizing system performance. Regular maintenance and upgrades are essential to ensure that the ERP system remains up-to-date and functional.
Integration Requirements for ERP Systems
Integration requirements are a crucial component of ERP systems as they determine how well the system can communicate and collaborate with other software applications within an organization. When considering integration requirements for an ERP system, it is essential to assess the following key elements:
1. Data Integration: One of the primary integration requirements for an ERP system is the ability to seamlessly integrate data from various sources and applications. This includes incorporating data from legacy systems, third-party software, and other databases into the ERP system. The ERP system should be able to consolidate and synchronize all data in real-time to provide a comprehensive view of the organization’s operations.
2. Application Integration: Another critical integration requirement for ERP systems is the ability to integrate with other business applications, such as CRM systems, supply chain management software, and financial reporting tools. The ERP system should be able to exchange data and workflows with these applications to streamline business processes and improve efficiency. Seamless application integration ensures that the ERP system can work in harmony with other software solutions to enhance overall performance.
3. API Capabilities: API (Application Programming Interface) capabilities are becoming increasingly important for ERP systems as organizations seek to connect their software applications and systems in a more flexible and scalable manner. An ERP system with robust API capabilities allows for easy integration with third-party applications, cloud services, and IoT devices. APIs enable data to be shared securely and efficiently between different systems, enhancing collaboration and enabling real-time data exchange. Organizations should look for an ERP system that offers a wide range of API capabilities to support their evolving integration needs.
4. Customization Options: Organizations may have unique integration requirements that necessitate the ability to customize and extend the functionality of their ERP system. Customization options, such as the ability to develop custom integrations, modify existing workflows, and create tailored reports, are essential for meeting specific business needs. An ERP system that offers extensive customization options allows organizations to adapt the system to their requirements and integrate it seamlessly with their existing software ecosystem.
5. Scalability and Flexibility: As organizations grow and evolve, their integration requirements may change. Therefore, it is crucial for an ERP system to be scalable and flexible to accommodate future integration needs. The system should be capable of handling increasing data volumes, supporting additional users, and integrating with new applications as the business expands. A scalable and flexible ERP system ensures that organizations can adapt to changing integration requirements and continue to derive value from their software investment.
Security requirements for ERP systems
When it comes to ERP systems, security is of utmost importance. ERP systems often contain sensitive and confidential data, such as financial information, customer data, and intellectual property. It is crucial to have robust security measures in place to protect this data from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyber threats.
One of the key security requirements for ERP systems is access control. This involves restricting access to the system and its data to only authorized users. User authentication mechanisms, such as passwords, biometric authentication, and multi-factor authentication, should be implemented to verify the identity of users before granting them access to the system. Role-based access control is also essential, where users are assigned specific roles and permissions based on their job responsibilities.
Another important security requirement for ERP systems is data encryption. Data encryption ensures that data is stored and transmitted securely, making it unreadable to unauthorized users. Encryption should be used for sensitive data at rest (stored data) and in transit (data being transmitted between systems or users). Strong encryption algorithms should be utilized to protect data from being compromised.
Regular security audits and monitoring are also necessary for ERP systems. Security audits help identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the system, allowing for timely remediation of issues. Continuous monitoring of system activity and user behavior can help detect any suspicious activities or unauthorized access attempts. Intrusion detection systems and security information and event management (SIEM) tools can be used for real-time monitoring and analysis of security events.
Furthermore, secure communication channels are essential for ERP systems. Data exchanged between different modules of the ERP system, as well as with external systems or users, should be encrypted to prevent eavesdropping and interception of sensitive information. Secure protocols, such as HTTPS for web communication and VPN for remote access, should be implemented to ensure secure data transmission.
It is also vital to have disaster recovery and backup procedures in place for ERP systems. In the event of a security breach, data loss, or system failure, backup copies of data should be readily available to restore the system to its previous state. Regular backups should be performed and stored securely offsite to prevent data loss due to unforeseen events.
In conclusion, security is a critical aspect of ERP systems, and it is essential to implement stringent security requirements to safeguard sensitive data and protect the system from cyber threats. By adhering to access control measures, data encryption, security audits, secure communication channels, and disaster recovery procedures, organizations can ensure the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of their ERP systems.
Scalability requirements for ERP systems
When considering scalability requirements for ERP systems, it is important to take into account the future growth of your business. Scalability refers to the ability of the ERP system to handle increased levels of data, users, and transactions as the business expands. It is crucial to choose an ERP system that can easily scale up or down based on the needs of the organization.
One key aspect of scalability is the ability to handle a large volume of data. As your business grows, the amount of data generated and processed by the ERP system will also increase. The system should be able to efficiently store, retrieve, and process large amounts of data without sacrificing performance. This is especially important in industries where data analytics and reporting are crucial for decision-making.
Another important factor to consider is the scalability of the user interface. As more employees start using the ERP system, it should be able to support a larger number of concurrent users without experiencing performance degradation. The system should also provide customizable user interfaces to accommodate the varying needs and preferences of different users.
Scalability requirements also extend to the integration capabilities of the ERP system. As the business expands, there may be a need to integrate the ERP system with other applications or third-party services. The system should be able to easily integrate with new technologies and adapt to changing business requirements without causing disruptions to the existing processes.
Additionally, scalability requirements for ERP systems include the ability to support increased transaction volumes. As the business grows, there will be a higher number of transactions processed through the system on a daily basis. The ERP system should be able to handle this increased load without experiencing delays or downtime, ensuring smooth and efficient operations.
In conclusion, when evaluating ERP systems, it is essential to consider scalability requirements to ensure that the system can grow along with the business. By choosing a system that can easily scale up in terms of data handling, user interface support, integration capabilities, and transaction volume, businesses can future-proof their operations and adapt to changing needs. Scalability is a key factor in maximizing the potential of an ERP system and achieving long-term success for the organization.